Inclusive Education & Disability : उत्तराखंड पात्रता परीक्षा 2024 के लिए UTET के ऑनलाइन आवेदन खुल चुके हैं यदि आप उत्तराखंड टीईटी के लिए आवेदन करना चाहते हैं तो आप ऑनलाइन आवेदन कर सकते हैं और अपनी तैयारी शुरू कर सकते हैं क्योंकि उत्तराखंड टेट 2024 का पेपर अक्टूबर में होगा । आपकी तैयारी को मजबूत करने के लिए आज हम बाल विकास एवं शिक्षण शास्त्र से समावेशी शिक्षा और डिसेबिलिटी (Inclusive Education & Disability) टॉपिक को आपके लिए लेकर आए हैं ।
बाल विकास एवं शिक्षण शास्त्र के प्रश्न सभी शिक्षक पात्रता परीक्षा CTET,UPTET,UTET,HTET, MPTET आदि में पूछे जाते हैं । यदि आप भी शिक्षक भर्ती परीक्षा की तैयारी कर रहे हैं तो आपके लिए यह बाल विकास एवं शिक्षण शास्त्र के प्रश्न (UTET CDP MCQ in Hindi) बहुत ही उपयोगी होंगे ।
What is Inclusive Education (समावेशी शिक्षा)
समावेशी शिक्षा एक शैक्षिक दृष्टिकोण है जहाँ सभी क्षमताओं और पृष्ठभूमियों के छात्र एक ही कक्षा में एक साथ सीखते हैं। यह विविधता को मान्यता देता है और मूल्यवान मानता है, शिक्षा तक समान पहुँच को बढ़ावा देता है, और सभी छात्रों के लिए सीखने की बाधाओं को हटाता है।
Inclusive education refers to an educational approach where students of all abilities and backgrounds learn together in the same classes. It involves recognizing and valuing diversity, promoting equal access to education, and removing barriers to learning for all students.
समावेशी शिक्षा के सिद्धांत
- समानता और गैर-भेदभाव: सभी छात्रों को शिक्षा में भाग लेने और लाभ उठाने के समान अवसर मिलना चाहिए।
- विविधता को संसाधन मानना: कक्षा में विविधता को एक ताकत और सभी के लिए सीखने के अनुभव को समृद्ध करने वाले संसाधन के रूप में देखा जाता है।
- भागीदारी और सशक्तिकरण: छात्रों को सक्रिय रूप से अपनी शिक्षा में भाग लेने के लिए प्रोत्साहित किया जाता है, और उनकी आवाज और चुनावों का सम्मान किया जाता है।
- समर्थक वातावरण: एक समर्थक और लचीला सीखने का वातावरण तैयार किया जाता है जो छात्रों की विविध आवश्यकताओं को समायोजित करता है।
- सहयोगात्मक सीखना: छात्रों, शिक्षकों, माता-पिता और समुदाय के बीच सहयोग समावेशी शिक्षा की सफलता के लिए आवश्यक है।

Principles of Inclusive Education
- Equality and Non-Discrimination: All students should have equal opportunities to participate in and benefit from education.
- Diversity as a Resource: Diversity in the classroom is seen as a strength and a resource for enriching the learning experience for all.
- Participation and Empowerment: Students are encouraged to participate actively in their learning, and their voices and choices are respected.
- Supportive Environment: A supportive and flexible learning environment is created to accommodate the diverse needs of students.
- Collaborative Learning: Collaboration among students, teachers, parents, and the community is essential for successful inclusive education.
समावेशी शिक्षा को लागू करने की रणनीतियाँ
- अंतरित निर्देश: शिक्षण विधियों और सामग्री को छात्रों की विभिन्न सीखने की शैलियों और क्षमताओं को ध्यान में रखते हुए अनुकूलित करना।
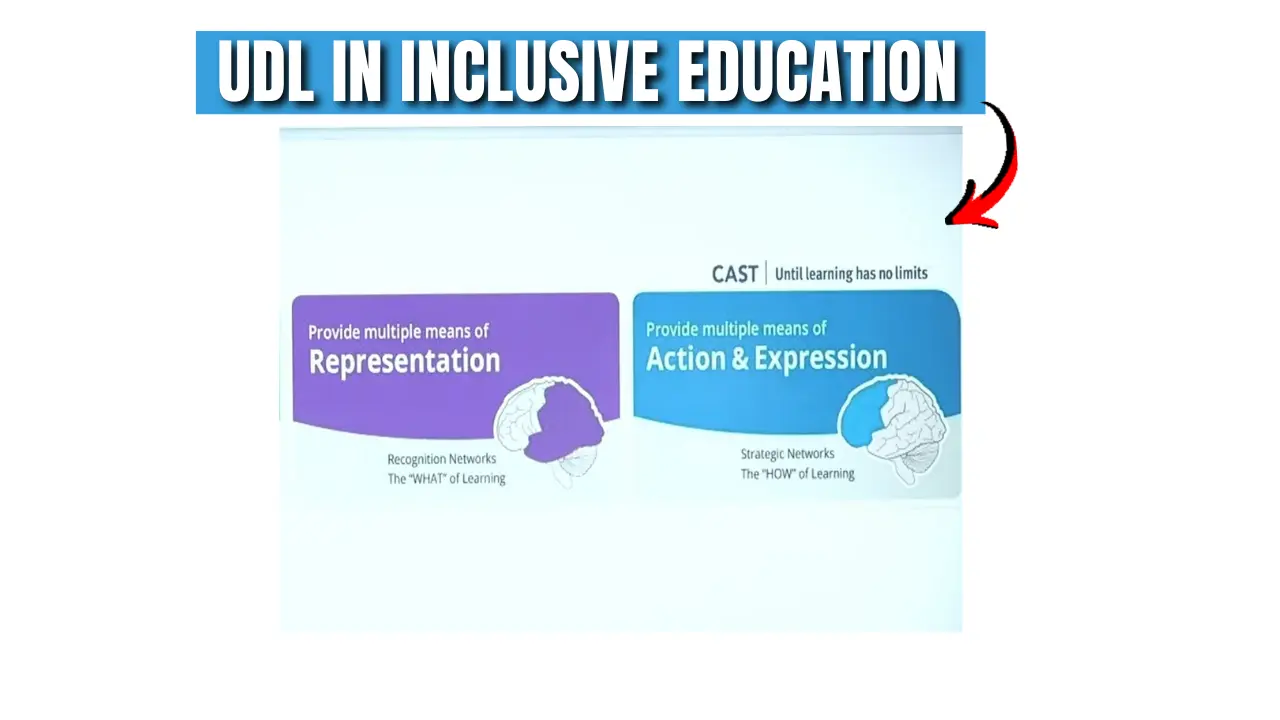
- सार्वभौमिक शिक्षा डिजाइन (UDL): पाठ्यक्रम और निर्देश को इस तरह से डिजाइन करना जो सभी छात्रों द्वारा पहुँचा, समझा, और उपयोग किया जा सके।
- व्यक्तिगत शिक्षा योजनाएँ (IEPs): छात्रों की विशिष्ट आवश्यकताओं को पूरा करने के लिए विशिष्ट, मापने योग्य, और प्राप्त करने योग्य लक्ष्य विकसित करना।
- सहपाठी सहायता और सहयोग: सहपाठी ट्यूटरिंग और समूह गतिविधियों को प्रोत्साहित करना ताकि एक समर्थक सीखने का वातावरण बनाया जा सके।
- व्यावसायिक विकास: शिक्षकों और कर्मचारियों को समावेशी शिक्षा के प्रभावी ढंग से लागू करने के लिए निरंतर प्रशिक्षण और संसाधन प्रदान करना।
Strategies for Implementing Inclusive Education
- Differentiated Instruction: Tailoring teaching methods and materials to accommodate the different learning styles and abilities of students.
- Universal Design for Learning (UDL): Designing curriculum and instruction that can be accessed, understood, and used by all students.
- Individualized Education Plans (IEPs): Developing specific, measurable, and attainable goals for students with disabilities to meet their unique needs.
- Peer Support and Collaboration: Encouraging peer tutoring and group activities to foster a supportive learning environment.
- Professional Development: Providing teachers and staff with ongoing training and resources to effectively implement inclusive education practices.
समावेशी शिक्षा के लाभ
- सुधारात्मक शैक्षिक परिणाम: समावेशी सेटिंग्स में छात्र व्यापक पाठ्यक्रम और उच्च उम्मीदों के कारण अकादमिक रूप से बेहतर प्रदर्शन करते हैं।
- सामाजिक और भावनात्मक विकास: समावेशी शिक्षा सामाजिक इंटरैक्शन और मित्रता को बढ़ावा देती है, जिससे छात्रों के सामाजिक कौशल और आत्म-सम्मान में सुधार होता है।
- सांस्कृतिक दक्षता: छात्र विविधता की अधिक समझ और प्रशंसा विकसित करते हैं, जिससे वे एक बहुसांस्कृतिक समाज के लिए तैयार होते हैं।
- कलंक में कमी: समावेश विकलांगताओं से जुड़े कलंक को कम करता है और विभिन्नताओं के प्रति स्वीकृति और सम्मान को बढ़ावा देता है।
Benefits of Inclusive Education
- Improved Academic Outcomes: Students in inclusive settings often perform better academically due to exposure to a broader curriculum and higher expectations.
- Social and Emotional Growth: Inclusive education fosters social interaction and friendships, enhancing students’ social skills and self-esteem.
- Cultural Competence: Students develop a greater understanding and appreciation of diversity, preparing them for a multicultural society.
- Reduction in Stigma: Inclusion reduces the stigma associated with disabilities and promotes acceptance and respect for differences.
What is Disability (विकलांगता)
विकलांगता एक शारीरिक, मानसिक, संवेदी, या संज्ञानात्मक स्थिति है जो किसी व्यक्ति की दैनिक गतिविधियों को करने और समाज में पूर्ण रूप से भाग लेने की क्षमता को काफी हद तक सीमित कर देती है।
A disability is a physical, mental, sensory, or cognitive condition that significantly limits a person’s ability to perform everyday activities and participate fully in society.
विकलांगताओं के प्रकार
- शारीरिक विकलांगताएँ: वे विकार जो किसी व्यक्ति की गतिशीलता या शारीरिक क्षमता को प्रभावित करते हैं (जैसे, सेरेब्रल पाल्सी, रीढ़ की हड्डी की चोटें)।
- संवेदी विकलांगताएँ: वे विकार जो संवेदनाओं से संबंधित होते हैं जैसे दृष्टि और सुनने की क्षमताएँ (जैसे, अंधापन, बहरापन)।
- बौद्धिक विकलांगताएँ: वे विकार जो संज्ञानात्मक कार्यक्षमता को प्रभावित करते हैं (जैसे, डाउन सिंड्रोम, ऑटिज़्म स्पेक्ट्रम डिसऑर्डर)।
- मानसिक स्वास्थ्य विकलांगताएँ: वे स्थितियाँ जो किसी व्यक्ति के भावनात्मक और मनोवैज्ञानिक स्वास्थ्य को प्रभावित करती हैं (जैसे, अवसाद, सिज़ोफ्रेनिया)।
- सीखने की विकलांगताएँ: वे विकार जो किसी व्यक्ति की सीखने और जानकारी को संसाधित करने की क्षमता को प्रभावित करते हैं (जैसे, डिस्लेक्सिया, एडीएचडी)।
Types of Disabilities
- Physical Disabilities: Impairments that affect a person’s mobility or physical capacity (e.g., cerebral palsy, spinal cord injuries).
- Sensory Disabilities: Impairments related to senses such as sight and hearing (e.g., blindness, deafness).
- Intellectual Disabilities: Impairments that affect cognitive functioning (e.g., Down syndrome, autism spectrum disorder).
- Mental Health Disabilities: Conditions that affect a person’s emotional and psychological well-being (e.g., depression, schizophrenia).
- Learning Disabilities: Disorders that affect a person’s ability to learn and process information (e.g., dyslexia, ADHD).
कानूनी ढांचा और नीतियाँ
- विकलांग व्यक्तियों के अधिकार अधिनियम, 2016 (भारत): एक व्यापक कानून जो विकलांग व्यक्तियों के लिए समान अधिकार और अवसर सुनिश्चित करता है, जिसमें शिक्षा, रोजगार, और सामाजिक समावेश शामिल हैं।
- विकलांग व्यक्तियों के अधिकारों पर संयुक्त राष्ट्र संधि (CRPD): एक अंतरराष्ट्रीय संधि जो विकलांग व्यक्तियों के सभी मानव अधिकारों का पूर्ण और समान आनंद बढ़ावा देती है, उनकी रक्षा करती है, और सुनिश्चित करती है।
- समावेशी शिक्षा नीतियाँ: राष्ट्रीय और राज्य स्तर की नीतियाँ जो मुख्यधारा के स्कूलों में विकलांग छात्रों के समावेश को अनिवार्य करती हैं और समावेशी शैक्षिक वातावरण बनाने के लिए दिशानिर्देश प्रदान करती हैं।
Legal Framework and Policies
- The Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016 (India): A comprehensive law that ensures equal rights and opportunities for persons with disabilities, including access to education, employment, and social inclusion.
- The UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD): An international treaty that promotes, protects, and ensures the full and equal enjoyment of all human rights by persons with disabilities.
- Inclusive Education Policies: National and state-level policies that mandate the inclusion of students with disabilities in mainstream schools and provide guidelines for creating inclusive educational environments.
विकलांग छात्रों के लिए समावेशी शिक्षा में बाधाएँ
- रवैये में बाधाएँ: विकलांगताओं के बारे में नकारात्मक दृष्टिकोण और गलतफहमियाँ भेदभाव और बहिष्कार का कारण बन सकती हैं।
- भौतिक बाधाएँ: अव्यवस्थित स्कूल के बुनियादी ढाँचे और सुविधाएँ विकलांग छात्रों को पूरी तरह से शिक्षा में भाग लेने से रोक सकती हैं।
- पाठ्यक्रम में बाधाएँ: एक कठोर पाठ्यक्रम जो विविध सीखने की आवश्यकताओं को समायोजित नहीं करता, वह विकलांग छात्रों की शैक्षिक प्रगति को बाधित कर सकता है।
- समर्थन सेवाओं की कमी: विशेष शिक्षा सेवाओं, सहायक तकनीकों, और प्रशिक्षित कर्मचारियों की अपर्याप्त उपलब्धता समावेशी शिक्षा को लागू करने में बाधा डाल सकती है।
Barriers to Inclusive Education for Students with Disabilities
- Attitudinal Barriers: Negative attitudes and misconceptions about disabilities can lead to discrimination and exclusion.
- Physical Barriers: Inaccessible school infrastructure and facilities can prevent students with disabilities from fully participating in education.
- Curriculum Barriers: A rigid curriculum that does not accommodate diverse learning needs can hinder the educational progress of students with disabilities.
- Lack of Support Services: Insufficient availability of special education services, assistive technologies, and trained personnel can impede the implementation of inclusive education.
समर्थन प्रणालियाँ और सेवाएँ
- सहायक तकनीकें: उपकरण और डिवाइस जो विकलांग छात्रों को पाठ्यक्रम तक पहुँचने और सीखने की गतिविधियों में भाग लेने में मदद करते हैं (जैसे, स्क्रीन रीडर, श्रवण यंत्र, गतिशीलता सहायक)।
- विशेष शिक्षा सेवाएँ: विशेष शिक्षकों और चिकित्सकों द्वारा प्रदान की गई सेवाएँ जो विकलांग छात्रों की सीखने और विकास में सहायता करती हैं।
- माता-पिता की भागीदारी: माता-पिता को शिक्षा प्रक्रिया में शामिल करना ताकि वे सूचित हों और अपने बच्चे की शिक्षा में सक्रिय रूप से शामिल हों।
- समुदाय समर्थन: अतिरिक्त समर्थन प्रदान करने और समावेशी वातावरण बनाने के लिए समुदाय संगठनों और संसाधनों के साथ सहयोग करना।
सीखने की विकलांगताओं के प्रकार
सीखने की विकलांगताएँ न्यूरोलॉजिकल विकार होते हैं जो किसी व्यक्ति की जानकारी प्राप्त करने, प्रक्रिया करने, संग्रहीत करने, या प्रतिक्रिया देने की क्षमता को प्रभावित करते हैं। ये आजीवन स्थितियाँ होती हैं और अकादमिक प्रदर्शन और दैनिक गतिविधियों पर महत्वपूर्ण प्रभाव डाल सकती हैं। यहाँ सीखने की विकलांगताओं के मुख्य प्रकार हैं:
Types of Learning Disabilities
Learning disabilities are neurological disorders that affect a person’s ability to receive, process, store, or respond to information. They are lifelong conditions and can significantly impact academic performance and everyday activities. Here are the main types of learning disabilities:
1. डिस्लेक्सिया
परिभाषा: डिस्लेक्सिया एक भाषा-आधारित सीखने की विकलांगता है जो पढ़ने और संबंधित भाषा-आधारित प्रसंस्करण क्षमताओं को प्रभावित करती है।
विशेषताएँ:
- सटीक और/या प्रवाहमय शब्द मान्यता में कठिनाई।
- खराब वर्तनी और डिकोडिंग क्षमताएँ।
- पढ़ने की समझ में समस्याएँ।
- धीमी पढ़ने की गति और घटित पढ़ने की प्रवाह।
- निर्देशों को समझने और पालन करने में कठिनाई।
- लिखित अभिव्यक्ति में कठिनाई।
हस्तक्षेप:
- फोनीक्स-आधारित निर्देश।
- मल्टीसेंसरी शिक्षण विधियाँ।
- पढ़ने के हस्तक्षेप और ट्यूटिंग।
- सहायक तकनीक जैसे टेक्स्ट-टू-स्पीच सॉफ़्टवेयर का उपयोग।
1. Dyslexia
Definition: Dyslexia is a language-based learning disability that affects reading and related language-based processing skills.
Characteristics:
- Difficulty with accurate and/or fluent word recognition.
- Poor spelling and decoding abilities.
- Problems with reading comprehension.
- Slow reading rate and reduced reading fluency.
- Challenges in understanding and following instructions.
- Difficulty with written expression.
Interventions:
- Phonics-based instruction.
- Multisensory teaching methods.
- Reading interventions and tutoring.
- Use of assistive technology like text-to-speech software.
2. डिस्ग्राफिया
परिभाषा: डिस्ग्राफिया लेखन क्षमताओं को प्रभावित करती है, जिसमें हस्तलेखन, टाइपिंग, और वर्तनी शामिल हैं।
विशेषताएँ:
- खराब हस्तलेखन, अक्सर अवैध।
- असंगत अंतराल और कागज पर खराब स्थानिक योजना।
- वर्तनी और विचारों को कागज पर व्यवस्थित करने में कठिनाई।
- सूक्ष्म मोटर कौशल में समस्या।
- लेखन कार्यों के दौरान थकान और निराशा।
हस्तक्षेप:
- सूक्ष्म मोटर कौशल सुधारने के लिए व्यावसायिक चिकित्सा।
- लेखन को संरचना देने के लिए ग्राफिक आयोजकों का उपयोग।
- टाइपिंग और टाइपिंग निर्देश।
- सहायक तकनीक जैसे शब्द प्रोसेसर।
2. Dysgraphia
Definition: Dysgraphia affects writing abilities, including handwriting, typing, and spelling.
Characteristics:
- Poor handwriting, often illegible.
- Inconsistent spacing and poor spatial planning on paper.
- Difficulty with spelling and organizing thoughts on paper.
- Trouble with fine motor skills.
- Fatigue and frustration during writing tasks.
Interventions:
- Occupational therapy to improve fine motor skills.
- Use of graphic organizers to structure writing.
- Keyboarding and typing instruction.
- Assistive technology like word processors.
3. डिस्कल्कुलिया
परिभाषा: डिस्कल्कुलिया एक सीखने की विकलांगता है जो किसी व्यक्ति की संख्याओं को समझने और गणित के तथ्यों को सीखने की क्षमता को प्रभावित करती है।
विशेषताएँ:
- संख्या अवधारणाओं और प्रतीकों को समझने में कठिनाई।
- गिनती और संख्याओं को पहचानने में समस्याएँ।
- बुनियादी अंकगणितीय संचालन (जोड़, घटाव, गुणा, भाग) करने में कठिनाई।
- मानसिक गणना और अनुमान में कठिनाई।
- गणितीय तथ्यों को समझने और याद रखने में समस्याएँ।
हस्तक्षेप:
- दृश्य सहायक और मैनिपुलेटिव का उपयोग।
- गणित ट्यूटिंग और विशेष निर्देश।
- गणित समस्याओं को छोटे, प्रबंधनीय चरणों में विभाजित करना।
- प्रौद्योगिकी का उपयोग जैसे कैलकुलेटर और गणित सॉफ़्टवेयर।
3. Dyscalculia
Definition: Dyscalculia is a learning disability that affects a person’s ability to understand numbers and learn math facts.
Characteristics:
- Difficulty understanding number concepts and symbols.
- Problems with counting and recognizing numbers.
- Challenges in performing basic arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division).
- Difficulty with mental math and estimation.
- Problems with understanding and remembering math facts.
Interventions:
- Use of visual aids and manipulatives.
- Math tutoring and specialized instruction.
- Breaking down math problems into smaller, manageable steps.
- Use of technology like calculators and math software.
4. श्रवण प्रसंस्करण विकार (APD)
परिभाषा: APD श्रवण जानकारी को संसाधित करने के तरीके को प्रभावित करता है, जिससे ध्वनियों की व्याख्या करना, विशेष रूप से भाषण, मुश्किल हो जाता है।
विशेषताएँ:
- शोर वाले वातावरण में मौखिक निर्देशों का पालन करने में कठिनाई।
- समान ध्वनियों के बीच अंतर करने में समस्याएँ।
- पढ़ने, वर्तनी, और समझ में कठिनाई।
- मौखिक रूप से प्रस्तुत जानकारी को याद रखने में कठिनाई।
- मौखिक उत्तेजनाओं पर विलंबित प्रतिक्रिया।
हस्तक्षेप:
- दृश्य सहायक और लिखित निर्देशों का उपयोग।
- सीखने के वातावरण में पृष्ठभूमि शोर को कम करना।
- श्रवण प्रशिक्षण कार्यक्रम।
- भाषण और भाषा चिकित्सा।
4. Auditory Processing Disorder (APD)
Definition: APD affects how the brain processes auditory information, making it difficult to interpret sounds, especially speech.
Characteristics:
- Difficulty following spoken directions, especially in noisy environments.
- Problems distinguishing between similar sounds.
- Challenges with reading, spelling, and comprehension.
- Trouble remembering information presented verbally.
- Delayed response to verbal stimuli.
Interventions:
- Use of visual aids and written instructions.
- Reduction of background noise in learning environments.
- Auditory training programs.
- Speech and language therapy.
5. दृश्य प्रसंस्करण विकार (VPD)
परिभाषा: VPD दृश्य जानकारी की व्याख्या करने के तरीके को प्रभावित करता है, जिससे पढ़ने, लिखने, और गणित पर असर पड़ता है।
विशेषताएँ:
- समान दिखने वाले अक्षरों और संख्याओं के बीच अंतर करने में कठिनाई।
- स्थानिक जागरूकता और दृश्य स्मृति में समस्याएँ।
- दृश्य जानकारी को समझने और याद रखने में कठिनाई।
- पढ़ने की समझ और शब्दों को पहचानने में कठिनाई।
- समन्वय में समस्याएँ और ठीक मोटर कौशल की आवश्यकता वाले कार्यों में कठिनाई।
हस्तक्षेप:
- बड़े प्रिंट और उच्च कंट्रास्ट सामग्री का उपयोग।
- दृश्य सहायक और संगठनात्मक उपकरण।
- दृष्टि चिकित्सा और अभ्यास।
- अनुकूलन जैसे ऑडियोबुक्स और मौखिक निर्देश।
5. Visual Processing Disorder (VPD)
Definition: VPD affects how the brain interprets visual information, impacting reading, writing, and math.
Characteristics:
- Difficulty distinguishing between similar-looking letters and numbers.
- Problems with spatial awareness and visual memory.
- Trouble understanding and remembering visual information.
- Challenges with reading comprehension and recognizing words.
- Poor coordination and difficulty with tasks requiring fine motor skills.
Interventions:
- Use of larger print and high-contrast materials.
- Visual aids and organizational tools.
- Vision therapy and exercises.
- Adaptations like audiobooks and oral instructions.
6. गैर-मौखिक सीखने की विकलांगताएँ (NVLD)
परिभाषा: NVLD किसी व्यक्ति की गैर-मौखिक संकेतों को समझने और उपयोग करने की क्षमता को प्रभावित करती है, जिससे सामाजिक कौशल और स्थानिक समझ में असर पड़ता है।
विशेषताएँ:
- शारीरिक भाषा, चेहरे के हावभाव, और आवाज के स्वर की व्याख्या करने में कठिनाई।
- स्थानिक जागरूकता और मोटर समन्वय में समस्याएँ।
- गणित में कठिनाई, विशेष रूप से ज्यामिति और दृश्य-स्थानिक कार्य।
- खराब संगठनात्मक कौशल और योजना में समस्याएँ।
- मजबूत मौखिक कौशल लेकिन व्यावहारिक, दैनिक कार्यों में कठिनाई।
हस्तक्षेप:
- सामाजिक कौशल प्रशिक्षण और कोचिंग।
- मोटर कौशल के लिए व्यावसायिक चिकित्सा।
- संरचित दिनचर्या और संगठनात्मक उपकरण।
- दृश्य सहायक और चरण-दर-चरण निर्देश।
6. Nonverbal Learning Disabilities (NVLD)
Definition: NVLD affects a person’s ability to understand and use nonverbal cues, impacting social skills and spatial understanding.
Characteristics:
- Difficulty interpreting body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice.
- Problems with spatial awareness and motor coordination.
- Challenges with math, particularly geometry and visual-spatial tasks.
- Poor organizational skills and trouble with planning.
- Strong verbal skills but difficulty with practical, everyday tasks.
Interventions:
- Social skills training and coaching.
- Occupational therapy for motor skills.
- Structured routines and organizational tools.
- Visual aids and step-by-step instructions.
Aphasia
Aphasia is a communication disorder that affects a person’s ability to process language, including speaking, understanding, reading, and writing. It usually occurs after a stroke or brain injury that damages the language centers of the brain.
Types of Aphasia
- Broca’s Aphasia (Non-fluent Aphasia):
- Characteristics: Difficulty in speech production, short and halting sentences, omission of small words (like “is” or “the”), relatively good comprehension.
- Causes: Damage to the frontal lobe of the brain, specifically Broca’s area.
- Wernicke’s Aphasia (Fluent Aphasia):
- Characteristics: Fluent but nonsensical speech, difficulty understanding spoken language, use of incorrect or made-up words.
- Causes: Damage to the temporal lobe of the brain, specifically Wernicke’s area.
- Global Aphasia:
- Characteristics: Severe impairment in both speech production and comprehension, limited to no speech, poor reading and writing abilities.
- Causes: Extensive damage to the language areas of the brain.
- Anomic Aphasia:
- Characteristics: Difficulty finding the right words (especially nouns and verbs), relatively good comprehension and grammar.
- Causes: Damage to various parts of the brain, often less severe.
Symptoms
- Difficulty speaking and forming sentences.
- Trouble understanding spoken language.
- Difficulty reading and writing.
- Using incorrect words or making up words.
- Repetition of words or phrases.
Interventions
- Speech and language therapy to improve communication skills.
- Use of alternative communication methods (e.g., gestures, drawing).
- Family education and support to facilitate better communication.
- Technological aids like speech-generating devices.
Apraxia
Apraxia is a motor disorder that affects a person’s ability to plan and execute voluntary movements, despite having the desire and physical ability to perform the movements. It can impact speech (apraxia of speech) or other motor functions (limb apraxia).
Types of Apraxia
- Apraxia of Speech (Verbal Apraxia):
- Characteristics: Difficulty coordinating the movements needed for speech, inconsistent speech errors, struggling to pronounce words correctly, knowing what to say but unable to articulate it properly.
- Causes: Damage to the brain regions involved in speech planning and execution, often due to stroke, head injury, or neurodegenerative diseases.
- Limb Apraxia:
- Characteristics: Difficulty coordinating arm and hand movements, trouble with tasks like waving, buttoning a shirt, or using tools.
- Causes: Damage to the parietal lobes or other brain areas involved in motor planning, often due to stroke or brain injury.
Symptoms
- Difficulty performing tasks or movements when asked, even though they understand the task.
- Inconsistent errors in movement.
- Inability to imitate movements or gestures.
- Difficulty with daily activities requiring coordinated movements.
Interventions
- Occupational therapy to improve motor skills and coordination.
- Physical therapy to strengthen muscles and improve movement.
- Speech therapy for apraxia of speech to practice speech production.
- Use of visual and verbal cues to aid in movement planning.
- Adaptive strategies and tools to assist with daily tasks.
Read More : UTET CDP MCQ in Hindi | उत्तराखंड TET के लिए महत्वपूर्ण प्रश्न
